When talking about male fertility, most people think of the sex hormone testosterone. But there are actually a number of hormones that drive the male reproductive process. When these hormones are out of balance, it can affect fertility, which is why testing for hormonal imbalance can be helpful if you’re trying to conceive.
Over one-third of infertility cases are caused by male reproductive issues. Hormonal testing for male fertility can provide crucial clues about whether or not hormonal imbalances are contributing to difficulty conceiving. This article will explain what male fertility hormonal testing entails, which hormones are tested, and how hormone testing can provide a roadmap to improving your fertility, including testing for hormonal imbalance.
What is male hormonal testing?
In addition to a semen analysis, hormonal testing is typically recommended when a couple is having trouble conceiving. Usually, a healthcare provider will draw a sample of blood from the patient. Their blood then undergoes a series of tests to assess the overall balance of the hormonal system.
Male hormonal testing evaluates the levels of testosterone, FSH, LH, and in some cases prolactin, which all work together to control sperm production, sexual function, and sex drive. If imbalances are found, hormone therapy or other medication may be recommended to improve hormone balance or increase the number or quality of sperm. Assisted reproductive techniques can also be used to improve chances of fertility.
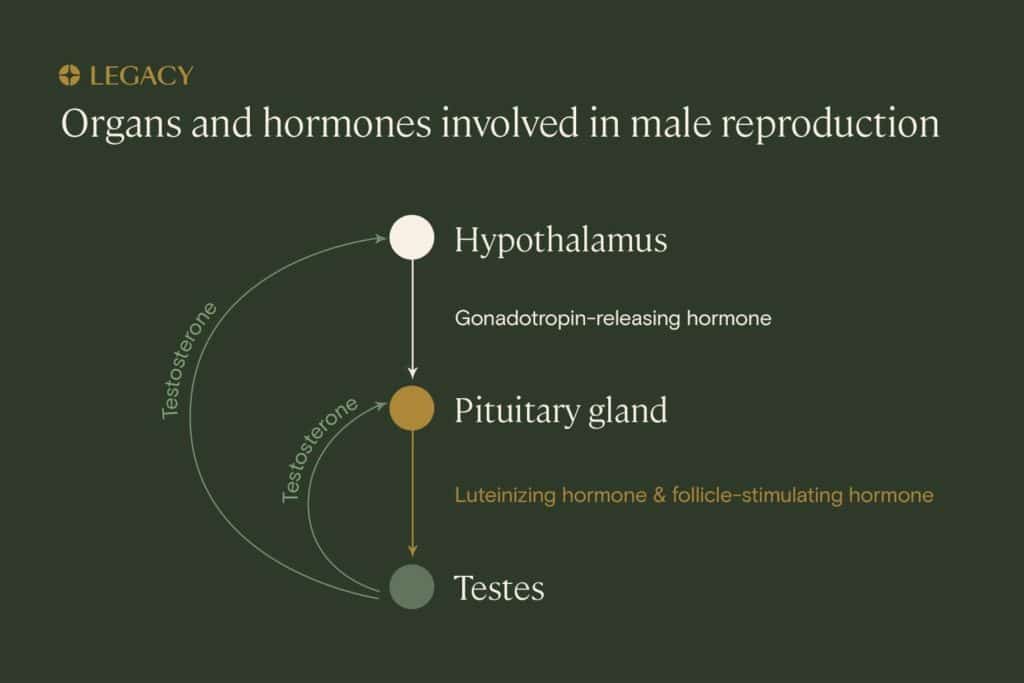
Male fertility hormone levels and reproduction
The testicles, the pituitary gland, and the hypothalamus produce key hormones that drive sperm production and sexual function. When there is too much or too little of these hormones, individuals may experience azoospermia, in which there is no sperm in the semen, or low sperm counts, oligospermia or the more severe cryptozoospermia. Any of these conditions can negatively affect fertility.
The three most important hormones impacting reproduction are follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and testosterone. Because the hormones work collaboratively, if there is an imbalance of one hormone, it can cause an imbalance in another. Testing for hormonal imbalances typically assess these three hormones.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and male fertility
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is crucial to spermatogenesis, or sperm production. Produced by the pituitary gland, FSH is known as a gonadotropin, a hormone that acts on the gonads (the ovaries or testes) to produce and mature eggs or sperm.
Certain conditions that affect the pituitary gland, the reproductive organs, or the hypothalamus part of the brain, which sends key messages to the pituitary gland, can lead to FSH imbalances resulting in infertility. Low FSH in men correlates with low sperm quality and reduced sperm production, while high FSH in men can be a sign of testicular damage or failure. Male hormonal testing can help identify potential imbalances.
There are a variety of possible causes for these imbalances, including:
- Advanced paternal age
- Injuries to the testes or the glands involved in hormone production
- Genetic issues such as Klinefelter syndrome
- Certain tumors
As a collaborative hormone, FSH works closely with luteinizing hormone to produce sperm and testosterone. FSH levels are typically checked if an individual has a low total motile sperm count or low sperm count. Identifying FSH levels is an integral part of testing for hormonal imbalances.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Like FSH, luteinizing hormone (LH) is also produced by the pituitary gland in the brain, and is part of a pathway comprising the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, and the gonads. LH stimulates the Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone. Therefore, LH supports sexual desire and sperm production.
Also like FSH, LH can negatively impact fertility when it is too low or too high. A deficiency in LH can lead to a deficiency in testosterone, which may then reduce sex drive and sperm production. If your LH levels are too high, this may indicate that your testicles have been damaged due to chemotherapy, radiation, infection, or alcohol abuse, or you potentially have Klinefelter syndrome, a genetic disorder that affects sexual development and often leads to infertility. Hormonal testing for infertility typically entails analyzing luteinizing hormone levels.
Testosterone
Testosterone, often called “T,” is a male sex hormone with many roles. Testosterone is responsible for the creation and growth of male sex organs (the penis and testes), and for the development of secondary “male” physical characteristics during puberty, such as muscle growth, body hair, and a deeper voice. Testosterone also also plays a key role in male fertility by regulating the sex drive and supporting sperm production.
When levels of testosterone are abnormally low, also known as hypogonadism, libido (sex drive) and erectile function may be negatively affected. Low testosterone levels, or hypogonadism, have been found in approximately 15% of subfertile men. However, it’s not impossible to conceive with low testosterone.
Supplementing with testosterone isn’t a solution. Remember that careful balance of hormones we discussed? Adding outside testosterone to the mix can throw the balance off, negatively affecting FSH production and therefore impairing sperm production. In many cases, people on testosterone replacement therapy will become completely infertile.
In some cases, exercise, dietary changes, supplementation, and even stress reduction can all naturally increase testosterone levels. Testosterone is one of several key hormones identified with male hormonal testing.
Benefits of male hormone testing for fertility
Dealing with fertility issues can be a stressful experience, especially when you don’t know why you’re having trouble. Even if you consider yourself healthy, your hormone profile may not reflect that. Hormonal testing can help eliminate uncertainty or a sense of helplessness when trying to conceive by detecting hormonal imbalances that may be contributing to infertility. Testing for hormonal imbalances can also help find a clear path forward for couples looking to conceive.
If imbalances are found, doctors can then outline potential treatment options, which may include medication like Clomid, supplementation, or assisted reproductive technology like in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI).
There are also other important health implications when it comes to hormonal testing. For instance, brain tumors that affect the pituitary gland or other parts of the skull base can lead to abnormal hormone levels and require treatment. Hormonal testing can alert you to the presence of these tumors. In middle-aged and older men, lower testosterone concentrations are associated with a higher incidence of cardiovascular events.
Hormonal testing can also be a turning point for your lifestyle, as healthy habits play a role in hormone regulation. Research shows that the following factors help keep your fertility hormones balanced:
- Eating a varied and balanced diet with plenty of fruits and vegetables
- Cutting back on sugar
- Engaging in moderate intensity aerobic exercise
- Limiting alcohol use
- Giving up smoking
- Getting enough sleep
If you and your partner are having trouble conceiving, it’s best for both of you to get tested. This isn’t to initiate a blame game, but rather to set you up with a plan. Hormone testing for infertility is typically a good first step before trying to conceive, along with semen analysis.
Signs a hormone test is needed for male fertility
Difficulty creating a pregnancy is one of the main reasons someone might have their hormones tested. Infertility is defined as an inability to achieve a healthy pregnancy after a year of actively trying to conceive with unprotected intercourse.
If you’re unsure if male-factor infertility is involved in your case, the first step is to get your sperm tested. This allows you to check if you have poor semen parameters like low sperm count, sperm motility issues, or sperm morphology issues. Once you know that you have problems with sperm production, you may want to check if your hormones are contributing to those problems. This process may feel somewhat like a scavenger hunt.
Here are some signs that may also indicate a hormonal imbalance:
- Abnormal semen analysis results, especially low sperm count
- Reduced body hair growth
- Thinning hair
- Weight gain or weight loss
- Low sex drive
- Erectile dysfunction
- Overdevelopment of breast tissue
- Fatigue
Hormonal testing costs
There are a variety of ways to check your hormone levels, including at-home male hormone testing kits and tests performed at a clinic. If you choose to go to a clinic, the price may range from $500 to $1,500, depending on how many hormones are tested. There may also be clinical consultation fees. Insurance may cover the costs of male hormone testing if it is recommended by a physician.
At-home male hormone testing kits also vary in cost (and may also vary in quality), but typically hover around the $200 range. There are test kits for testosterone alone, which are lower in cost at around $50–$70 — but as we’ve discussed above, testosterone is just one of the hormones involved in male fertility.
How can I check my fertility?
Testing your sperm is one vital way to evaluate your fertility, even before male hormone testing. Legacy’s at-home semen analysis kit is the most scientifically advanced at-home semen test, which allows you to test your sperm health from the comfort of your own home.
The semen analysis kit evaluates sperm count/concentration, motility, and morphology and is conducted in CLIA-certified labs by a team of experienced scientists. All results are reviewed by our medical staff and you also have access to fertility advisors for extra support.
Whether you’re having trouble conceiving or you simply want to understand your fertility better, testing your sperm is a good place to start. The earlier you find out if you have an underlying issue, the earlier you can address it — and go on to build a happy, healthy family.