Your sperm is your future
As seen in








Fertility declines with each birthday
Past 35, you’re more likely to deal with infertility — and your child has a higher risk of conditions like autism.

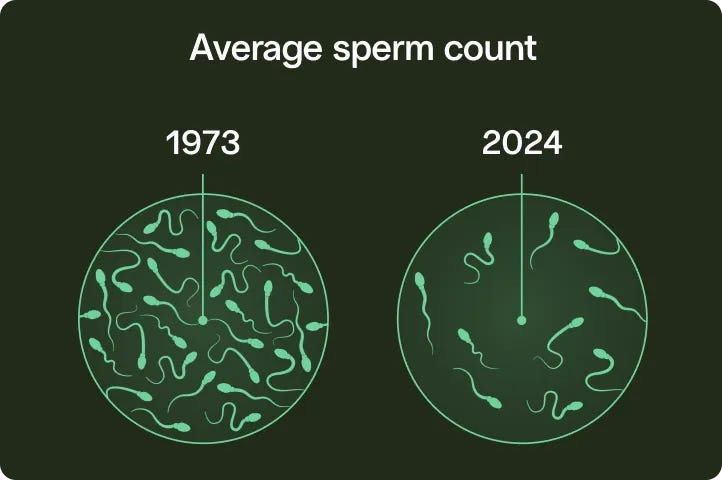
Our sperm is not okay
Sperm counts have dropped over 50% since the 1970s, thanks to chemicals, plastics, and our modern lifestyles.
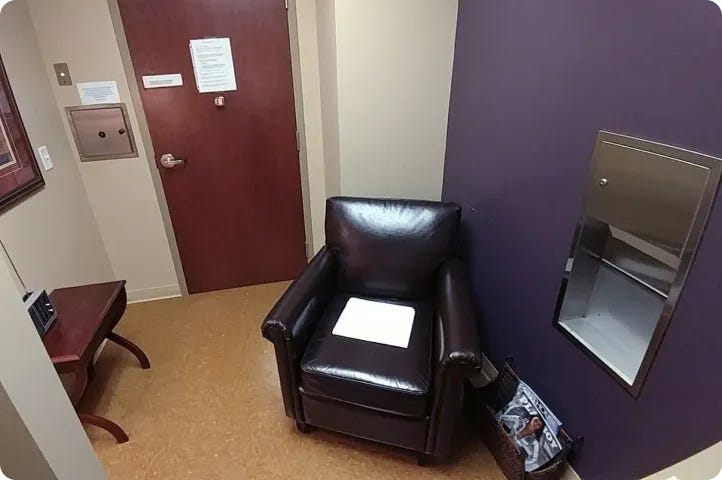
Clinics are awkward and expensive
With the old-school approach, you wait months for an appointment in the communal “collection room” (yikes).

Test your sperm. Preserve it at its peak. Without leaving home.
Get started
From checkout to lab in less than a week
10x faster than a traditional clinic. Get the data you need to get pregnant faster, faster — or freeze your sperm without delaying upcoming medical treatments.
Save over 60% compared to clinics
We’re making future family planning an option for all. Sperm freezing starts at $145 per year, and we’re in network with most major insurance plans and benefits.
Security and privacy at every step
Your kit arrives in discreet packaging, your results are available on a private virtual dashboard, and your sample is stored in multiple locations for redundancy.

We’ve supported over 30,000 future parents
Trusted by top fertility experts, the US military, and people like you.
2024
Best Option for
Sperm Testing
& Freezing
It was super simple and my insurance covered it.
Austin
TRT patient

Legacy is a game changer in the male fertility space.
4.9
130+ Google Business reviews
Mail-in kits can be a simple way to screen for any underlying sperm problem. This is a great option if you are not comfortable taking a specimen to the lab.Stanton Honig, MD, Professor of Clinical Urology

This company has changed my life. I almost gave up on having a child... I got a rep the same day I reached out. He set everything up for me. HIGHLY RECOMMEND.
Quan
Verified client

I want the option for kids later
Freezing your sperm can help you have healthy children, whenever you’re ready.
Learn moreI want the option for kids later

I want to grow my family soon
Testing your sperm can help you conceive faster, identify issues that make conception difficult, and explore more fertility planning options.
Learn moreI want to grow my family soon

I want to understand my health
Sperm quality is a biomarker of your overall health. It can indicate a higher risk of heart disease, cancer, and even premature death.
Learn moreI want to understand my health
Unbox your fertility future
Modern sperm health starts with a simple at-home kit.
Don’t leave family to chance.
Get started

