If you’re dealing with low testosterone, you’ve probably heard of testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) as a treatment. However, the side effects of TRT, such as infertility, means it isn’t a good fit for everyone.
We’ll take a look at several alternatives to testosterone replacement therapy that may help boost your testosterone levels.
Key takeaways
- Testosterone replacement therapy is the main treatment for hypogonadism, but it can cause side effects including infertility, leading some people to look for other options.
- Alternatives to testosterone replacement therapy include the medications clomiphene citrate and fluoxymesterone as well as lifestyle changes like losing weight, limiting alcohol, and getting sufficient sleep.
- The best testosterone alternative for you will depend on your medical conditions, your tolerance of side effects, and your plans for growing your family.
TRT vs. alternatives
Testosterone replacement therapy is a treatment that supplements the testosterone in your blood through patches, gels, implants, or oral tablets of exogenous (external) testosterone.
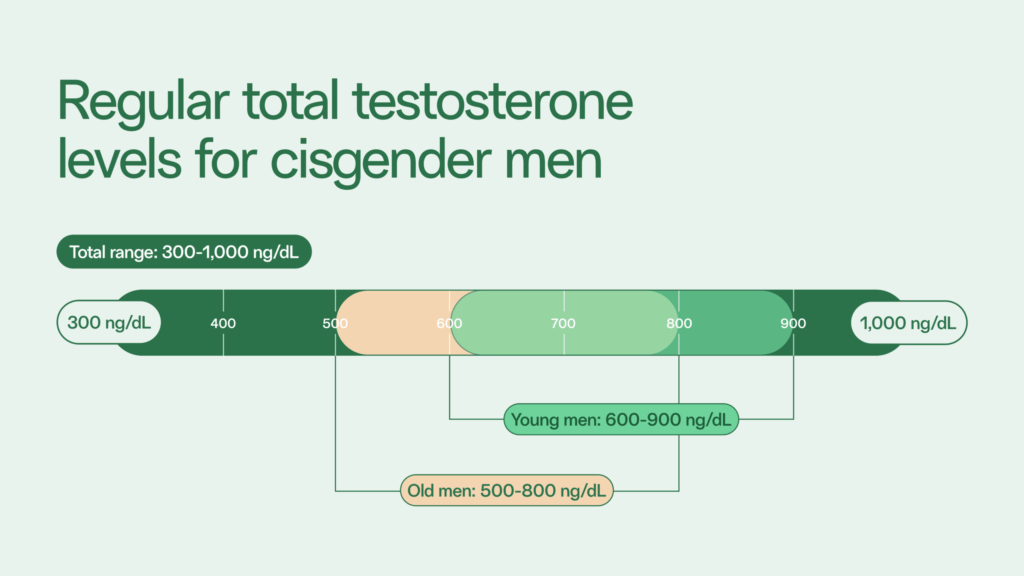
TRT is the primary treatment for male hypogonadism or “low T.” Low T may be diagnosed if your testosterone levels are below 300 ng/dL and you experience symptoms of low testosterone, such as erectile dysfunction or reduced muscle mass.
A 2017 study suggested that approximately 0.9 to 2.9% of men in the US use TRT.1 Still, it’s not the only treatment option for low-T.
Side effects of TRT
Research has found that, for most men, TRT is an effective way to improve testosterone levels and feel better.2 There is even some evidence that testosterone is involved in longevity. In one study, men who had been treated were half as likely to die in the 4 years after they started TRT.3
However, many men seek an alternative to testosterone therapy due to the unwanted side effects of TRT. Potential side effects of TRT include:
- infertility
- enlarged prostate
- liver damage
- erythrocytosis (a condition where your body produces too many red blood cells, thickening your blood)
- difficulty sleeping
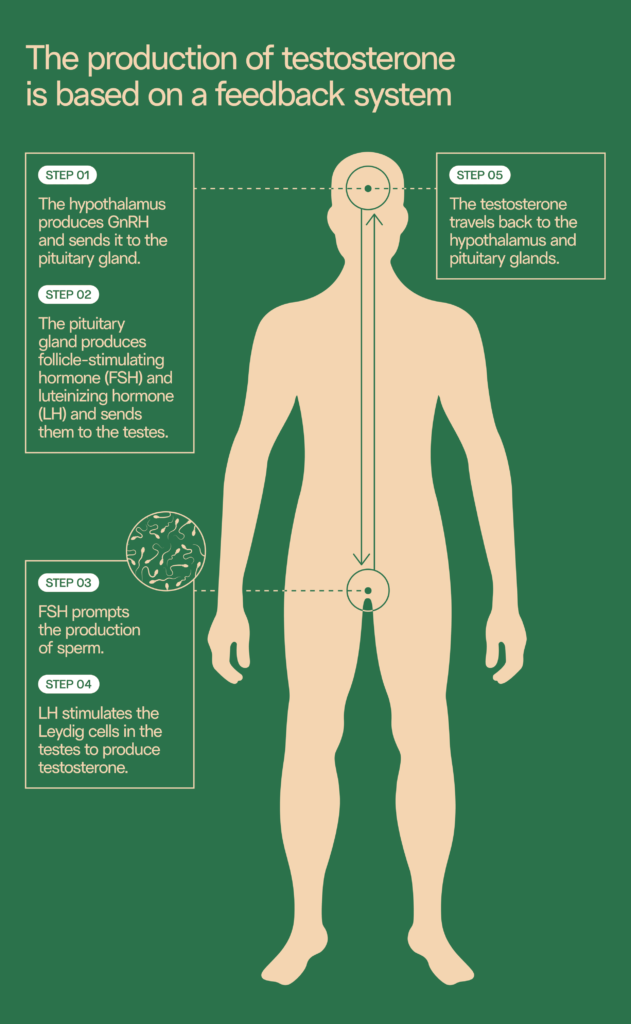
Many men are surprised to hear that taking testosterone can cause infertility. While testosterone plays an important role in reproduction, using external testosterone to boost your testosterone levels interferes with the balance of other male fertility hormones, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). LH and FSH drive sperm production, so taking TRT may stop sperm production entirely.
Research indicates that testosterone led to azoospermia, or the lack of sperm in the semen, in upwards of 65% of men after 4 months.4 While the effect may be reversible, it’s best to avoid TRT if you want a family in the future, or to freeze your sperm before beginning TRT.
If you’re trying to grow your family or are concerned about other side effects of TRT, you may wish to consider alternatives to testosterone replacement therapy to treat low T.
Alternative treatments for low testosterone
The best testosterone alternative will depend on your specific health conditions, your tolerance for side effects, and your goals for treating your condition (such as the desire to preserve your fertility).
Clomiphene citrate to improve testosterone levels
Clomiphene citrate (CC) is one possible medication you can try as an alternative to TRT. Sold as Clomid or Serophene, it’s a selective estrogen receptor modulator that stimulates LH and FSH, which in turn lead your body to produce more testosterone.
Research indicates that Clomid may be effective for people with low testosterone. Though hypogonadism is currently an off-label use of clomiphene citrate, a 2018 literature review suggested that it and other alternatives are effective and should be considered before TRT.5
And for those concerned about fertility, clomiphene has an added bonus: it may boost sperm production along with testosterone. One study of 47 men taking 50 mg of clomiphene citrate every other day found that testosterone increased and semen parameters improved among almost all participants after two weeks.6
In another study of 86 men with hypogonadism, taking either 25–50 mg of clomiphene citrate every other day for an average of 19 months increased participants’ testosterone levels and improved symptoms of low T.7 There were also no significant side effects, leading the authors to suggest that the medication may be an effective, safe, and fertility-preserving alternative to TRT.
A longer study of 153 men with hypogonadism also found that treatment with clomiphene citrate increased testosterone levels, and that the increase persisted after 8 years in those who continued treatment.8 Furthermore, 74% of participants saw improvements in their low T symptoms, and there were few side effects.
If you’re considering Clomid for low testosterone levels, talk to your doctor about any side effects and contraindications.
Fluoxymesterone to improve testosterone levels
Fluoxymesterone, a hormone that mimics testosterone, is marketed under the brand name Halotestin. It’s used as an oral steroid to build muscle mass, but is also available as a prescription to treat hypogonadism that’s caused by certain medical conditions and to help start puberty in males experiencing a delay.
However, some research suggests that fluoxymesterone may suppress testosterone and sperm production instead, and more studies need to be done.9
Fluoxymesterone can also cause some side effects similar to those of TRT. Side effects in people with sperm may include:
- reduced fertility
- breast enlargement
- sex drive changes
- headache
- anxiety or depression
- tingling feeling
- rash
- trouble breathing
- stomach pain
- nausea
- fluid retention
If you regularly take too much fluoxymesterone, stopping it may also lead to withdrawal symptoms.
With the side effects of fluoxymesterone and its questionable effectiveness, it may not be recommended as a treatment for hypogonadism, and other alternatives to testosterone replacement therapy may be better.10
Increasing testosterone naturally
Depending on the cause of your hypogonadism, you don’t necessarily need medication to boost your testosterone. Certain lifestyle changes may help increase your testosterone naturally. These include:
- Losing weight
- Exercising regularly
- Maintaining a healthy diet
- Taking supplements including vitamin D, zinc, and selenium
- Avoiding smoking
- Limiting alcohol
- Getting enough sleep
See our guide to increasing your testosterone naturally.
More research is needed on natural methods to boost testosterone. Still, even if these lifestyle changes don’t impact your testosterone, they may be worthwhile to help improve your overall health and fertility.
References
1. Bandari et al, “Marketing and Testosterone Treatment in the USA: A Systematic Review.” 2017.
3. Shores et a, “Testosterone treatment and mortality in men with low testosterone levels.” 2012.
6. Lo et al, “Alternatives to Testosterone Therapy: A Review.” 2018.
7. Katz et al, “Outcomes of clomiphene citrate treatment in young hypogonadal men.” 2011.
9. Jones et al, “The effects of fluoxymesterone administration on testicular function.” 1977.10. Khodamoradi et al, “Exogenous testosterone replacement therapy versus raising endogenous testosterone levels: current and future prospects.” 2020.