Influencers and doctors alike have made claims that eating more meat, meat-only diets, or even eating raw meat can boost men’s health, increase testosterone naturally, or improve fertility. Let’s take a look at the claims around the carnivore diet for men, and dive into the science.
Key takeaways
- Evidence suggests carnivore and keto diets may help people lose weight. However, experts believe these diets lack important nutrients for fertility and overall health.
- Studies looking at testosterone levels in men who eat different quantities of meat have found that increased meat consumption does not improve male hormone health.
- Research on the relationship between diet and sperm health has found that processed red meats may be detrimental to sperm, while vegetables and cereals may improve sperm health.
What is the “carnivore diet”?
Meat-heavy diets have been a men’s health trend for quite a few years, starting with the low-carb Atkins diet in the ‘90s. Today in 2024, you might see it called a “carnivore diet” or an “animal-based diet.”
The carnivore diet is essentially what it sounds like: a diet focused on eating animal products, especially meat. The diet has gained popularity on social media in recent years.
The carnivore diet can be seen as an extreme version of the ketogenic diet. Also known as the keto diet or just “keto,” it’s become popular over the last 10 years because of its ability to help with weight loss.
The keto diet involves eating 55–60% of your daily calories from fat, 20–35% from protein, and just 5–10% carbohydrates. That equates to around 20–50 grams of carbs per day (about 1 potato or ½ cup of pasta). The keto diet’s focus on fat and protein means you’ll likely eat a lot of meat, eggs, fish, and nuts.
The premise behind diets low in carbs is that, after a period of heavily restricting carbs, the body will begin breaking down fat and burning the resulting compounds, called ketones, for energy. Entering this stage is known as “ketosis.”



Claims about the carnivore diet for men
Online sources claim that meat-heavy diets like the carnivore diet and the keto diet have many benefits for men, including:
- Weight loss
- Improved digestion
- Better energy
- Higher testosterone levels
Psychologist Jordan Peterson has famously touted the merits of his all beef diet, while psychiatrist Paul Saladino has branded himself as the “CarnivoreMD” with a best-selling all-animal cookbook. Some proponents even purport the benefits of a raw meat diet for men.
The ketogenic diet was originally created to treat epilepsy, but the keto diet for men has been promoted as a possible way to lose weight, improve fertility, and increase testosterone levels.
Meat-heavy diets are based on the idea that our ancestors ate more meat, but it’s still unclear whether this is actually true.
Will a carnivore diet help me lose weight?
Both the keto and the carnivore diet have demonstrated the ability to help with weight loss. A survey-based study found that those who ate a carnivore diet for six or more months reported weight loss, improved well-being, and reduced symptoms from medical conditions.1
Research also shows that the keto diet may help with areas including diabetes, weight loss, and appetite control.2 Other studies indicate that keto diets may boost testosterone levels as well, likely thanks to the weight loss that keto dieters experience.3 It is well established that excess body weight is linked to lower testosterone levels.
Still, there are concerns that these diets may not provide sufficient nutrients for overall health. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, considered important sources of vitamins and fiber, are absent in the carnivore diet, and kept very low in the keto diet. The long-term health effects of these diets are unclear.
Will a carnivore diet improve testosterone?
While weight loss may improve testosterone levels, there is no evidence that consuming more meat is beneficial to male hormones.
One study looked at 189 young men and compared their dietary intake, categorized by processed red meats (like burgers and hot dogs), unprocessed red meats, organ meats, poultry, and fish.4 A similar study looked at dietary patterns among 206 young men in Spain.5
In both studies, those who consumed the most meat did not have higher testosterone levels than those in the lowest quartile of meat consumption.
| Average total testosterone levels | |
| Men with the lowest consumption of meat | 643 ng/dL |
| Men with the highest consumption of meat | 600 ng/dL |
Source: Maldonado-Cárceles et al, 2018.
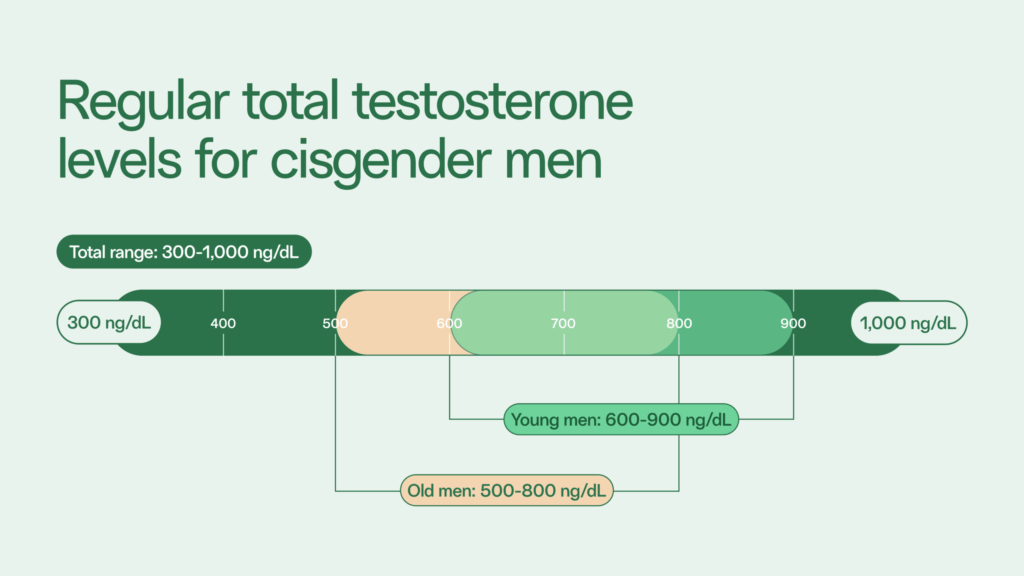
Normal total testosterone levels are 300–1,000 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL).
Interestingly, in late 2023, Dr. Paul Saladino — the aforementioned “Carnivore MD” — reported that he had quit the carnivore diet after 5 years, in part because his testosterone levels had dropped significantly.
In the article linked above, dietitian Sydney Greene speculates that “Dr. Saladino was possibly deficient in nutrients that are responsible for producing important hormones like testosterone.” Those nutrients include magnesium, found in leafy greens and avocados, and flavonoid antioxidants, found in berries, cherries, and pomegranates.
Learn more about diet and testosterone levels.

Will eating more meat improve sperm health?
The aforementioned studies, along with others, also looked at metrics of sperm health, including sperm count and quality. In several studies, eating processed red meats was associated with lower sperm counts.4–8
In most studies, eating unprocessed meat, such as steak or chicken, was not associated with decreased or improved sperm health. One study did find that eating more red meat decreased a man’s chance of getting his partner pregnant.9
Consumption of fish, shellfish, fruit, and vegetables, on the other hand, has been consistently associated with improved sperm counts and quality. In one study of nearly 3,000 Danish men, those with vegetarian diets or “prudent” diets (characterized by a higher consumption of fish, chicken, fruit, and vegetables) — in other words, those who ate less red meat and meat overall — had improved sperm parameters, compared to those who ate a Western or traditional Danish diet.
See 6 superfoods for male fertility.
In another study of 250 male patients from couples undergoing IVF, the foods most closely correlated with improved sperm health included:
- Grains
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Fish
In this study, meat consumption was correlated with lower sperm count and quality.9
Want to understand where your sperm health stands today? Try an at-home semen analysis for a full picture of your fertility.
Are there any health benefits to a raw meat diet for men?
In a word, no. Cooking may impact some nutrients in our food, but it also eliminates most of the pathogens often carried by raw meat. There are no benefits to eating raw meat over cooked meat.
References
- 1. Lennerz et al, “Behavioral Characteristics and Self-Reported Health Status among 2029 Adults Consuming a “Carnivore Diet.” 2021.
- 2. Dowis et al, “The Potential Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet: A Narrative Review.” 2021.
- 3. Furini et al, “Ketogenic state improves testosterone serum levels—results from a systematic review and meta-analysis.” 2022.
- 4. Afeiche et a, “Meat intake and reproductive parameters among young men.” 2014.
- 5. Maldonado-Càrceles et al, “Meat intake in relation to semen quality and reproductive hormone levels among young men in Spain.” 2018.
- 6. Mendiola et al, “Food intake and its relationship with semen quality: a case-control study.” 2008.
- 7. Afeiche et al, “Meat intake and semen parameters among men attending a fertility clinic.” 2014.
- 8. Nassan et al, “Association of Dietary Patterns With Testicular Function in Young Danish Men.” 2020.
- 9. Paes de Almeida Ferreira Braga et al, “Food intake and social habits in male patients and its relationship to intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcomes.” 2012.