If you’re trying to get a better understanding of your fertility, it’s time to become familiarized with sperm count. Sperm count is an important factor that can indicate the health of your sperm and overall fertility, and it is one of the parameters measured in a sperm analysis test. Having a healthy sperm count can increase your chances of conception. Read on to learn more about why sperm count plays a vital role in your fertility, and what you can do to increase your sperm count.
What is sperm count?
Sperm count and sperm concentration are two important male fertility factors. Sperm count is the total number of sperm in the entire semen sample. Sperm concentration, on the other hand, is the number of sperm per milliliter of semen (or the sperm “density” within the sample).
For example, if you produce a semen sample that is 3 milliliters in volume, your sperm count would be the total number of sperm in that 3 milliliter sample. If the total sperm count is 75 million, then we can use these two numbers to calculate sperm concentration—which, in this scenario, would be 25 million sperm per milliliter.
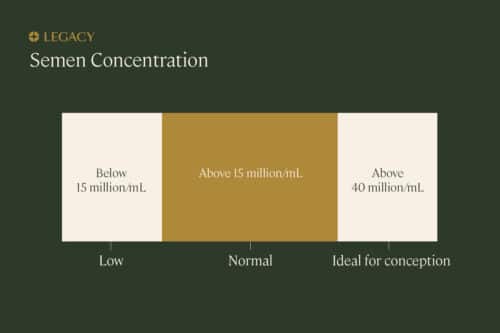
What is considered a healthy sperm concentration? According to the WHO guidelines, a sperm concentration of 15 million sperm per mL or greater is considered normal. However, other research indicates that a sperm concentration below 40 million sperm per mL may decrease chances of conception. In one study that tested 100 men, the vast majority of them had sperm counts above 60 million sperm per mL.

Why is sperm count important?
Sperm count is an important male fertility factor because your chances of conceiving with your partner decreases with a low sperm count. As sperm travels through the fallopian tubes, many become lost before ever reaching the egg. A higher sperm count means that there is a greater chance of sperm reaching and fertilizing an egg.
While sperm count/concentration is far from the only determining factor for your fertility, it is tied to your chances of acheiving pregnancy. One study found that incresing sperm concentration was associated with increased chances of conception up to 40 million sperm per mL of semen. Another study found that total sperm count and sperm concentration were correlated with higher chances of conceiving and shorter time to pregnancy; 71% of subjects with a sperm concentration under 20 million per mL were able to achieve pregnancy within 6 months, compared to 83% of subjects with a concentration under 20 million per mL.
Testing your sperm count
For those who want to know how to check sperm count, it’s simple. You can assess your sperm count, along with other important male fertility factors, with a semen analysis. A semen analysis test can be performed in the comfort and privacy of your own home—making it easier than ever before to take charge of your health and journey into fatherhood.
Males who have low sperm count and concentration may be diagnosed with oligospermia. In some cases, a male may not have any sperm in their semen at all, a condition known as azoospermia.
What affects sperm count?
A low sperm count can be caused by a number of factors. Some root causes may be uncontrollable, such as genetics. But there are also many possible causes that are within your control, such as diet and lifestyle factors.
Age
Men have been known to father babies well into their 60s and beyond—but that doesn’t mean men don’t face their own biological clocks when it comes to fertility. Age affects male fertility, including a male’s sperm count and concentration.
In a study that observed 97 non-smoking men without known fertility issues, sperm count and concentration decreased by 4.7% per year of age.
Medical history
Your medical history also has an impact on your sperm count and overall fertility. If you have contracted an STD or STI in the past that went untreated for longer than it should have, it could have an impact on your fertility.
Certain medical procedures and medications can also affect sperm count. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and certain surgeries for cancers of the reproductive organs can lead towards a decrease in sperm count and have an effect on overall male fertility.
Other drugs can affect male fertility, too, such as: alpha blockers, NSAIDs, opiates, antipsychotics, corticosteroids, ketoconazole, some antibiotics, and SSRIs and similar antidepressants.
It’s rare, but there may be anatomical, congenital, or genetic issues that affect fertility, as well. One example is congenital absence of the vas deferens (CAVD), a condition in which the duct that delivers sperm from the testicles to the penis is missing or undeveloped. In that case, sperm are being produced in the testes, but never make it to the semen, so the patient will present with azoospermia.
Lifestyle
Your lifestyle choices play a big role in your fertility. Here’s a snapshot of key habits that can influence your sperm count and concentration.
- Smoking cigarettes: Smoking has been shown to have a negative effect on male fertility by reducing total sperm count, sperm concentration and motility. One study found that among healthy males, a 24% lower sperm concentration was found in smokers versus nonsmokers. Another study found that the relationship between smoking and sperm count may be dose-dependent—meaning that heavy smokers may see a greater reduction in sperm count than casual smokers.
- Alcohol consumption: While occasional social drinking is unlikely to have an impact on your fertility, habitual or binge drinking has been associated with lower sperm count. One study found that total sperm count and sperm concentration is negatively correlated with increasing alcohol intake; men who had 40 drinks or more per week had a 33% reduction in sperm count and concentration compared to men who had less than 5 drinks per week.
- Diet: A high intake of certain foods is associated with lower sperm counts, and certain nutrients may improve sperm count, concentration, and overall fertility. Studies show that diets high in processed meats, trans fats, added sugars, and refined grains, are associated with lower sperm counts, concentration, motility, and morphology. On the other hand, a higher amounts of fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats may increase the chance of high sperm count and concentration.
- Exercise habits: A sedentary lifestyle can have negative effects on many aspects of your health, including fertility. In a study that observed groups of men classed by body mass index (BMI), men in the overweight and obese categories has lower sperm count and concentration than those within normal weight ranges. Oligospermia and azoospermia were also more prevalent in obese patients compared with men within normal weight range.
Environmental factors
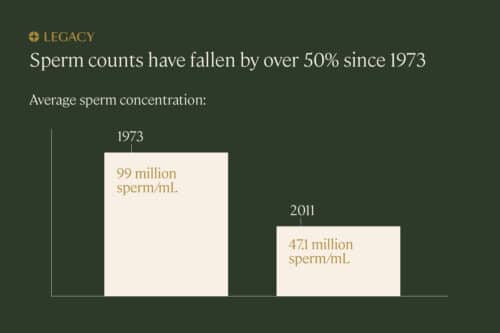
Research has shown that sperm counts have seen a significant decline—about 50%—between 1973 and 2011. One strong hypothesis for this decline is environmental factors such as exposure to pesticides, phthalates, parabens, and dioxins; all of these are “endocrine disruptors,” chemicals that interfere with the hormone system in our bodies. Many are found in products we use every day.
Animal and human studies show negative correlations between exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, even in utero, and fertility. One study found that offspring exposed to BPA had reduced sperm counts.
How to improve sperm count
One of the best ways to improve your sperm count is to make positive lifestyle changes. Here are a few steps you can take to improve sperm count:
- If you smoke, quit. The good news is that your sperm count and quality may begin to recover quickly—research shows that former smokers who quit more than six months ago might have similar semen parameters to non-smokers.
- Take a male fertility supplement, such as CoQ10 or vitamin C. One study showed a 167% increase in sperm count after three months of ashwagandha supplement, and another study showed sperm counts that doubled after two months of consistent Vitamin C supplementation. Learn more about male fertility supplements.
- Replace foods heavy in trans fat or added sugars with nutrient-rich sperm superfoods that have been shown to boost male fertility. Leafy greens like kale and spinach, bell peppers, and nuts have been shown to have a positive impact on sperm count and concentration.
- Get moving a few times a week with moderate intensity training. Even just walking 30–60 minutes, 4–6 times a week can improve your sperm count and motility.
- Prioritize quality sleep. Research shows that sleep deprivation can contribute to lower sperm count, so aim for getting 7-8 hours of quality, uninterrupted sleep each night. Learn more about sleep and male fertility.
For more tips on how to increase sperm count, check our guide to sperm improvement.
Do you have a healthy sperm count?
With Legacy’s at-home sperm analysis kit, you get a clear, easy-to-understand report of your sperm count and overall fertility—without any awkward clinic appointments or uncomfortable conversations. Get the insight and support you need, on your terms.



