In the U.S., 15% of couples have trouble conceiving in their first year of trying, and half the time, male-factor infertility is the cause. From poor sperm production to anatomical obstructions, there are many reasons why you or your partner may not be getting pregnant and male fertility testing can help find a diagnosis. For some, a simple semen analysis can point to sperm parameters that may need some improvement; for others, more advanced male fertility testing can reveal if a genetic disease is causing issues.
Doctors typically recommend that both partners get tested for infertility to see if there are multiple issues at play. Data shows that in one-third of infertile couples, the problem is with both partners. And age may also play a role, though male fertility declines more gradually.
When it comes to male fertility testing, some options are only available in a clinic, such as an ultrasound or testicular biopsy, but other male fertility testing options, like a semen analysis, can be performed from the comfort of your home.
Find out what male fertility testing entails, what male fertility testing options to consider, and which tests can be done at home.
Key takeaways
- Male fertility testing refers to a variety of medical examinations that can detect issues like poor sperm quality, hormonal imbalances, or genetic diseases.
- The primary male fertility testing option is a semen analysis, which measures the quantity and quality of your sperm across five key factors: volume, count, concentration, motility, and morphology.
- Other male fertility testing options include sperm DNA fragmentation analysis, hormonal testing, genetic testing, testicular biopsies, ultrasounds, and antisperm antibodies testing.
- Male fertility testing can be carried out at any point in the family planning process, but testing early is recommended so you can potentially improve sperm quality and increase your fertility chances.
What is male fertility testing?
Male fertility testing refers to a variety of medical examinations that can help detect fertility issues like poor sperm quality, hormonal imbalances, and more. While it’s common to seek out male fertility testing when infertility is suspected after a year of unsuccessfully trying for a child, male fertility testing can also be performed before trying to conceive. Not only can early testing help make the family planning process easier in the future and offer insights into potential treatments, it can also reveal other health issues. Studies show that poor sperm health is linked with health problems like high blood pressure, more body fat, and increased risk of developing diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
Male fertility testing options
A semen analysis is the most common and typically the first test performed when infertility is suspected, but it is not the only option. Testing for sperm DNA fragmentation can offer another layer of insight into sperm health, while hormone testing can reveal imbalances that may be affecting sperm production or even sexual function. Here are some male fertility testing options to consider:

Semen analysis
A semen analysis will measure the quantity and quality of your sperm across five key factors:
- Volume: how much semen you produce
- Count: total number of sperm in your sample
- Concentration: the ratio between semen and sperm
- Motility: how many of your sperm are moving
- Morphology: how many of your sperm are the proper size and shape
In the past, it was required to visit a clinic to provide a sperm sample and receive the results of your semen analysis. But sperm testing at home is becoming more accessible. Legacy’s at-home sperm testing kit allows you to collect and send your sample from home and receive results in as little as a week. Clinically validated as the most scientifically advanced at-home sperm testing, Legacy’s semen analysis is the only one of its kind to offer a post-thaw analysis, which is a quick freeze-and-thaw of a small percentage of your sperm to ensure your sample is viable for freezing.
Sperm DNA fragmentation analysis
A sperm DNA fragmentation analysis measures the percentage of abnormal or damaged DNA carried by sperm. This kind of damage can interfere with the sperm’s ability to properly fertilize an egg or for a healthy embryo to develop. Studies show that a high percentage of sperm with damaged DNA is associated with lower rates of pregnancy and higher risk of miscarriage. Though it is less common to test for DNA fragmentation in a routine semen analysis, Legacy’s at-home sperm testing kit offers a sperm DNA fragmentation analysis as an add-on option. Our labs use sperm chromatin dispersion (SCD), a well-established technique for identifying sperm DNA damage. And you don’t have to venture out to a specialist lab to perform the test as it can also be sent from home.
Male fertility hormone testing
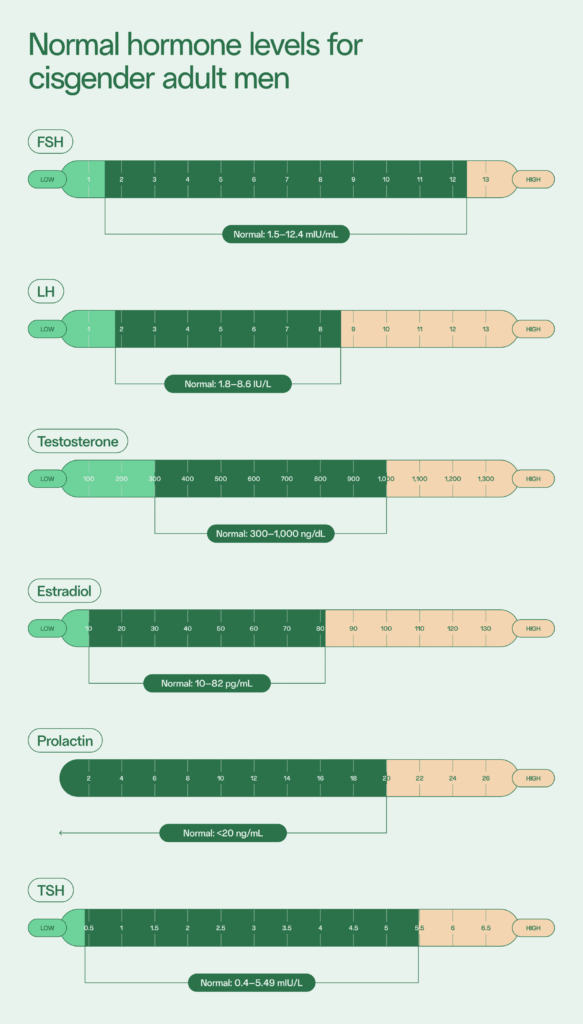
Typically performed with a simple blood sample, hormone testing detects imbalances that may be causing reproductive issues. Male hormonal testing assesses the levels of testosterone, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and, in some cases, prolactin, which work in concert to drive sperm production, sexual function, and libido. If imbalances are detected, your doctor may recommend taking male fertility supplements, making lifestyle changes, or even exploring assisted reproductive techniques.
Advanced male fertility testing options
In some cases, advanced male fertility testing is recommended, especially if an individual has a family history of a genetic disease, their sperm count is extremely low, or treatments to improve sperm quality and/or quantity have failed. Here are some advanced male fertility testing options to consider:
Genetic testing for male-factor infertility
While lifestyle habits and medical history can contribute to male fertility issues, for some people, genetics are at fault. Genetic testing analyzes the DNA within cells to find mutations associated with specific diseases. There are a variety of tests, which can be performed with a sample of blood or saliva. These tests may be able to find the following diseases related to male-factor infertility:
- Klinefelter syndrome: A genetic condition in which a biological male has an extra copy of the X chromosome, resulting in azoospermia (no sperm in semen), poor testicular growth, low testosterone levels, and low sex drive.
- Kallmann syndrome: A genetic disorder that causes hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (HH), in which little or no sex hormones are produced; delayed puberty; and undescended or partially descended testicles.
- Cystic fibrosis: A progressive genetic disease that impairs lung function and digestion; most biological males with this condition have a congenital absence of the vas deferens, which is the canal that carries sperm from the testicles to the penis.
- Y-chromosome microdeletions: A family of genetic disorders caused by missing genes in the Y-chromosome, which is associated with low sperm count, azoospermia, and a high percentage of abnormal sperm.
Testicular biopsy
During a testicular biopsy, a doctor removes tissues from the testicle to assess sperm production. The test is typically performed with a needle or by making a small incision. If test results indicate normal sperm production, the doctor will check if there’s a blockage or another problem affecting sperm transport. This test is typically performed if a semen analysis has detected abnormally low levels of sperm or the absence of sperm in semen.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound may detect internal issues affecting sperm production, such as varicocele, or enlarged veins in the scrotum, testicular size and volume, and obstructions of the vas deferens. An ultrasound may also find any abnormal masses or malignant tumors. Like a testicular biopsy, an ultrasound is usually performed if a semen analysis has found issues with sperm production.
Antisperm antibodies semen testing
Antisperm antibodies are proteins made by the immune system when it mistakes sperm for foreign invaders and tries to destroy them. Though rare, antisperm antibodies can be found in semen and blood, resulting in low sperm count, poor sperm motility, and negative sperm–egg interaction. To test for antisperm antibodies, your doctor may analyze a sperm sample or another bodily fluid, such as a blood serum sample.
Who should consider male fertility testing?
Whether you are at the beginning of your family planning journey or you’ve been trying for a while without success, male fertility testing is recommended at any point in the process. However, the benefit of undergoing male fertility testing early, maybe even before you start trying, is that it gives you the opportunity to devise a plan of action. This means that when you are ready, you will not encounter any unexpected obstacles.
Some male fertility issues can be reversed with healthy lifestyle changes such as improving your diet, establishing an exercise routine, and cutting back on smoking and alcohol. You may also find that a particular medication is affecting your fertility, at which point you can explore replacement options with your doctor. It’s important to note that it takes 70–90 days to produce new sperm. If your semen analysis indicates there’s room for improvement, you should implement lifestyle changes or supplementation immediately and test again in two to three months to gauge improvement.
Legacy’s at-home sperm testing options
Legacy offers a number of packages for at-home sperm testing, including one combining a semen analysis and sperm DNA fragmentation analysis. At-home sperm testing starts at $295 and may be covered by your insurance, especially if your doctor recommended you test. Financing is also available. Every semen analysis includes the option for sperm freezing.
There are also a number of bundles combining semen analyses with STI kits and sperm freezing, starting at $995.
You don’t have to wait until your partner is tested or you encounter problems. Testing your sperm from home is easy and will give you the head start you’ll appreciate when the time comes to start a family. Learn more about Legacy’s at-home sperm testing kits.